Dental 3D Printing: Accuracy vs. Resolution
When it comes to 3D printing applications in dentistry, accuracy is everything. It ensures that the printed models and devices fit perfectly, function as intended, and require minimal to no adjustments. However, many dental professionals mistakenly equate accuracy with resolution, leading to confusion about what truly matters when talking about 3D printing. In this article, we break down the key differences between accuracy and resolution in 3D printing, explaining why understanding these concepts is crucial for producing high-quality dental applications, from digital impressions to a dental 3D models and full-arch models.
What is Accuracy in 3D Printing?
Accuracy in 3D printing refers to how closely the final printed object matches the dimensions and design of its digital model. This means that if I print a crown with dimensions of 10 mm x 8 mm x 6 mm, the finished object should precisely match those measurements, without any deviation of even a fraction of a millimeter. 3D printer precision is a critical factor in determining the quality of 3D printed dental models and other dental applications. The trueness of the print, or how closely it matches the original design, is paramount in ensuring the success of dental procedures.
Key factors influencing accuracy and trueness
Accuracy in dental 3D printing is not determined by the printer alone – it is the result of a complete workflow, where every step can affect the final outcome. What matters most?
- Post-processing – even the highest-quality print can change its dimensions if it is washed improperly or cured incorrectly. Proper post-processing is critical for maintaining dimensional stability.
- Material selection – not all dental resins behave the same. Chemical composition, viscosity, and curing method determine how accurately a resin reproduces fine details and how stable it remains over time.
- Environmental conditions – temperature and humidity fluctuations may seem minor, but they affect process repeatability and, consequently, the final precision of the models.
- Model orientation – the positioning of the model on the build platform influences detail reproduction, shrinkage, and potential distortions. Even small adjustments in angle can significantly improve print quality and fit.
Each of these factors plays a key role in dental 3D printing. Optimizing every stage of the workflow ensures models that accurately reflect the patient’s real anatomy.
Dimensional accuracy
Dimensional accuracy is often measured as a tolerance range (e.g., +/- 37 µm) or as a percentage match to the original digital design. The most accurate 3D printing method for assessing dimensional accuracy and trueness is through the use of 3D scanning of the printed object. This allows for a precise comparison between the actual dimensions of the printed part and the original CAD/CAM model, which is crucial for applications like creating accurate models for dental implants.
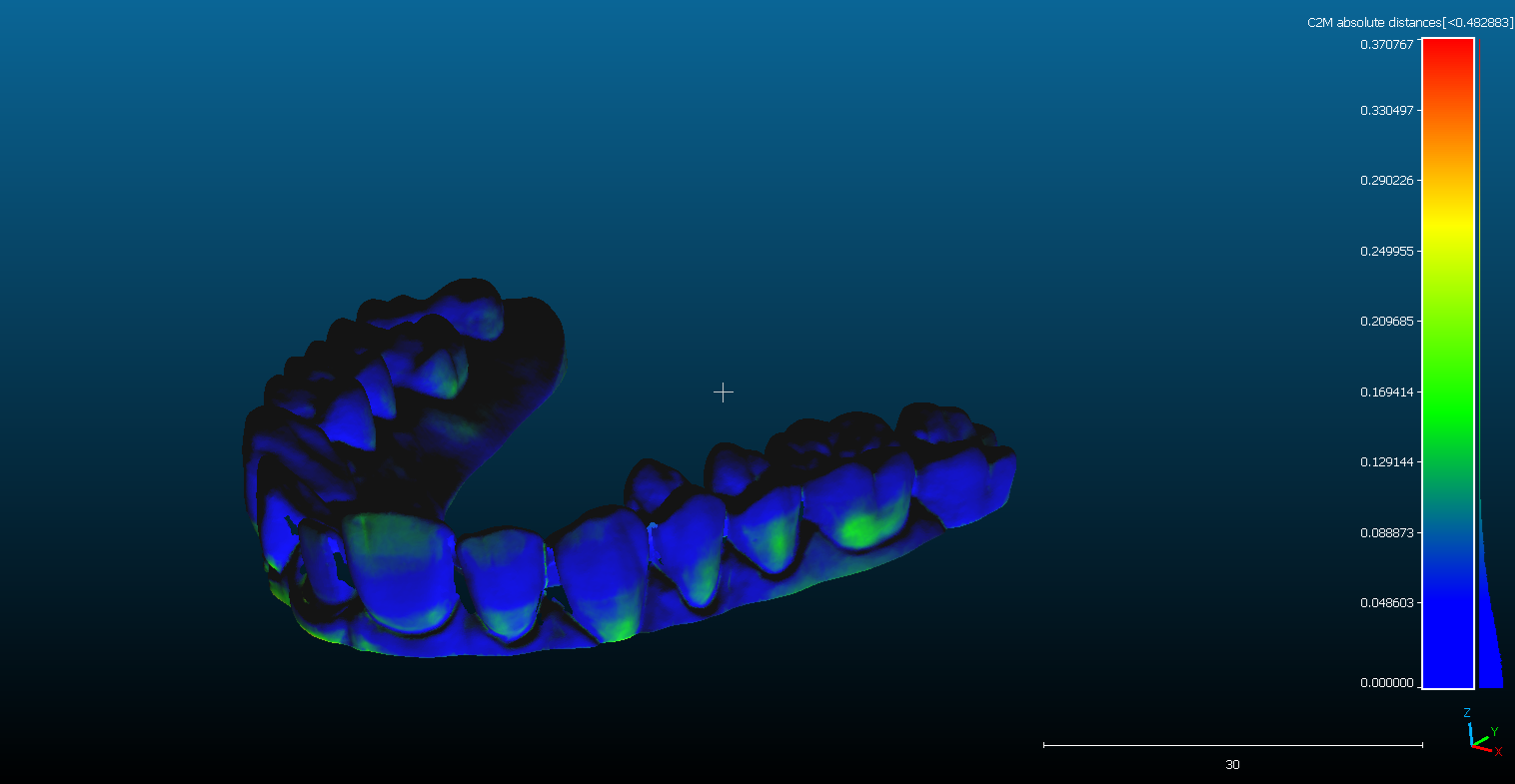
Comparison of a model printed with EVOCURE MODEL PRO resin against the CAD design, highlighting detail accuracy.
As shown in the image, 3D scanning allows for the visualization of any dimensional errors between the design and the print, enabling a precise evaluation of the overall workflow and 3D printer results. This level of precision is essential when considering how precise 3D printers are for dental applications, especially when creating accurate dental prosthetics.
What is Resolution in 3D Printing?
Resolution in 3D printing is all about how many tiny pixels make up the image on the screen during the printing process. This concept is particularly important in stereolithography (SLA), digital light processing (DLP) and LCD 3D printing methods commonly used in dentistry.

Example of a dental 3D printer LCD screen with 16K resolution. Source: elegoo.com
Think of it like this: the smaller the pixels, the more details you can capture in the final print. The XY resolution plays a crucial role in determining the precision of the printed object, which is especially important when creating intricate dental structures for implant procedures.
For example:
- A 4K resolution LCD printer (e.g., Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K) with a 6.1-inch screen might have a pixel size of approximately 35 microns (0.035 mm).
- The same 4K resolution on a larger 8.9-inch screen the pixels become bigger—about 50 microns (0.05 mm)
There is also another factor – pixel density, or how many pixels fit in each inch, also plays a big part. The higher the pixel density (PPI, or pixels per inch), the finer the details you can get. This is crucial when considering how precise 3D printers are for dental applications, including the creation of accurate 3D dental models.
To further illustrate, imagine drawing a picture on a piece of paper. Using tiny, precise lines will result in a highly detailed drawing, similar to having a higher resolution with smaller pixels. Conversely, using thick, bold lines might create a slightly blurry image, even though it represents the same basic picture.
For a more in-depth discussion on how resolution impacts the quality of your 3D prints, refer to our article: Resolution in Dental 3D Printing – 4K, 8K, 12K?
Key takeaway:
While resolution contributes to detail reproduction, accuracy and trueness focus on how well the printed object replicates the true shape and dimensions of the digital model. It’s crucial to remember that high resolution plays a big role in how detailed a print can be, it does not automatically guarantee perfect accuracy or trueness.
Why Layer thickness Isn’t the Same as Accuracy in 3D Printing
A common misconception in additive manufacturing revolves around the relationship between Z-axis resolution (layer thickness) and overall print accuracy and trueness. While finer layers undeniably produce smoother surfaces, minimizing the visible stair-step lines often associated with thicker layers, this improvement in surface quality does not directly translate to higher dimensional accuracy or trueness.
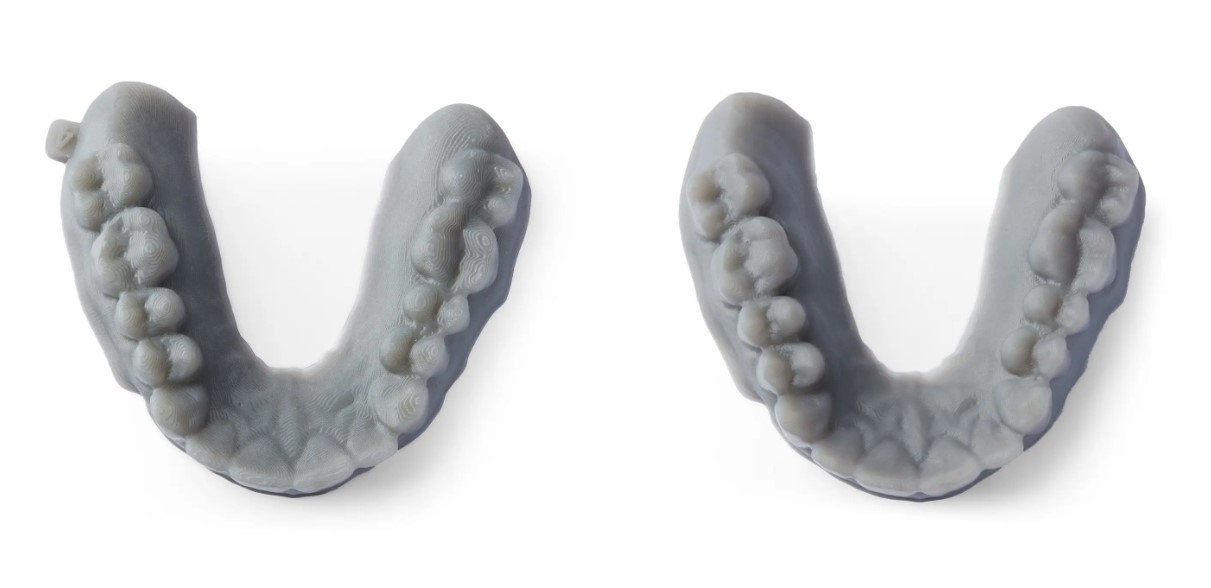
Printed at 200 µm for faster production of wax-ups and thermoformed appliances, and at 100 µm for maximum detail and smooth surfaces in high-precision aligners and premium dental models. Source: dental.formlabs.com
A common question we hear is: “What is your resin’s resolution — 50 µm or 100 µm?” That’s an understandable question, but it can be misleading. While a smooth surface finish matters in prosthetics and orthodontics — for crowns, veneers or wax-up models — resolution alone is neither the only nor the most important indicator of CAD/CAM conformity.
Accuracy of dental models is determined by multiple factors: the chemistry and behavior of the resin, the precision of the printer, and the specific printing technology used. These elements together define the final print quality and its clinical usefulness.
Key takeaway:
-
Dimensional accuracy is the measure that matters: it indicates how precisely a printed model reproduces the digital design across all axes, and it directly affects the fit of prosthetic and orthodontic work in the patient’s mouth.
-
Printer resolution ≠ dimensional accuracy: higher printer resolution may improve surface detail, but it does not guarantee that the printed part will match the intended dimensions.
-
Layer thickness alone does not determine accuracy: thinner layers smooth surfaces, but they do not inherently increase dimensional fidelity.
At Syntegre we prioritise dimensional accuracy and reliable print results. Every printing profile on our website is validated for dimensional conformity so customers can achieve predictable outcomes from their first print. We continuously update profiles to support new printers and workflows, maximising practical support for labs and clinics.
Check our available printing profiles — and if you have questions, contact us: we’re happy to help.


Kacper Włodarek
LCD screens in 3D printing: Monochrome vs RGB?
You're likely reading this article on a phone, tablet, or computer, and the first thing [...]


Kacper Włodarek
Resolution in Dental 3D Printing – 4K, 8K, 12K?
In dentistry, precision is paramount, whether for perfectly fitted prosthetics, diagnostic models, or tools supporting [...]


Przemysław Grabowski
3D printing resin filtration
Resin filtration is crucial in the 3D printing process as it significantly impacts the quality [...]